dental instruments pictures and names pdf
Dental Instruments: A Comprehensive Guide with Pictures and Names
This guide details essential dental tools‚ encompassing mirrors‚ explorers‚ scalers‚ forceps‚ and more‚ often found in comprehensive PDF resource lists for practical exams․
Dental instruments represent a cornerstone of modern dentistry‚ facilitating diagnosis‚ treatment‚ and surgical procedures with precision․ A comprehensive understanding of these tools – their names‚ functions‚ and proper handling – is paramount for dental professionals․ Numerous resources‚ often available as PDF guides‚ meticulously catalog these instruments‚ showcasing their diverse forms and applications․
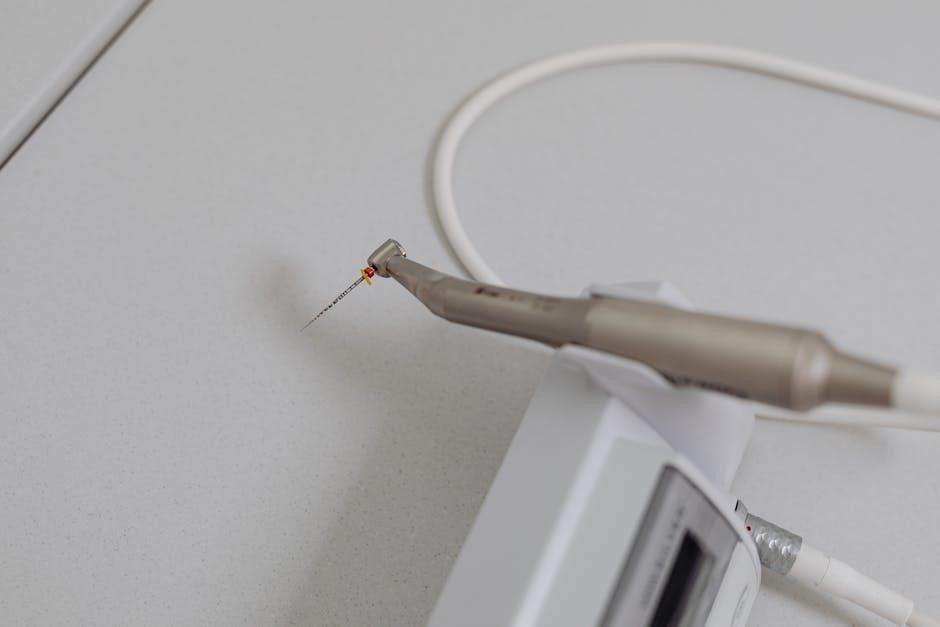

These guides frequently include detailed visuals‚ aiding in instrument identification and familiarization․ They cover everything from basic hand instruments like explorers and mirrors‚ used for initial examinations‚ to more complex tools employed in restorative and surgical dentistry․ The availability of PDF documents streamlines learning‚ providing readily accessible references for students and practitioners alike․ These resources often detail cleaning‚ disinfection‚ and sterilization protocols‚ crucial for maintaining patient safety and preventing cross-contamination within the dental clinic environment․
Basic Instrument Classification
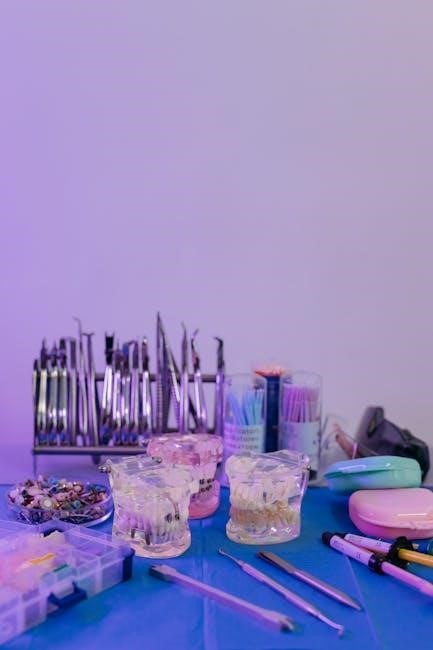

Dental instruments are broadly categorized based on their primary function and method of activation․ Hand instruments‚ requiring direct manual force‚ encompass diagnostic tools like explorers and mirrors‚ and operative instruments such as scalers and curettes․ Rotary instruments‚ powered by dental handpieces‚ include burs and bits used for cutting‚ grinding‚ and polishing․ Surgical instruments‚ like elevators and forceps‚ are employed in extractions and other surgical procedures․
PDF guides detailing these instruments often present classifications alongside illustrative pictures and names․ Sectional matrix systems and associated instruments form another key category․ Understanding these classifications is vital for selecting the appropriate tool for each clinical task․ Proper instrument arrangement‚ as detailed in some PDF resources‚ follows a logical sequence of use‚ enhancing efficiency and minimizing errors․ These classifications ensure organized workflows and contribute to optimal patient care․
Hand Instruments
Hand instruments represent the foundational tools in dentistry‚ relying entirely on the clinician’s manual dexterity․ These include a diverse range of implements for diagnosis and treatment․ Comprehensive PDF guides frequently showcase detailed pictures and names of these essential tools‚ aiding in identification and proper usage․ Common examples are explorers for cavity detection‚ mirrors for visibility‚ scalers to remove calculus‚ and curettes for root planing․
PDF resources often illustrate the precise blade designs and handle ergonomics of each instrument․ Chisels and mallets‚ alongside various forceps‚ also fall under this category․ Understanding the specific purpose of each hand instrument‚ as presented in visual guides‚ is crucial for effective and safe dental procedures․ Proper handling and maintenance‚ often detailed in accompanying PDF documentation‚ are paramount for longevity and performance․
Diagnostic Instruments
Diagnostic instruments are pivotal for initial patient assessment‚ enabling dentists to identify oral health issues․ PDF guides dedicated to dental instrumentation consistently feature clear pictures and names of these tools‚ facilitating accurate identification․ Key examples include dental mirrors‚ used for indirect vision‚ and explorers‚ designed to detect caries and calculus․ Probes are also essential for measuring pocket depths and assessing periodontal health․
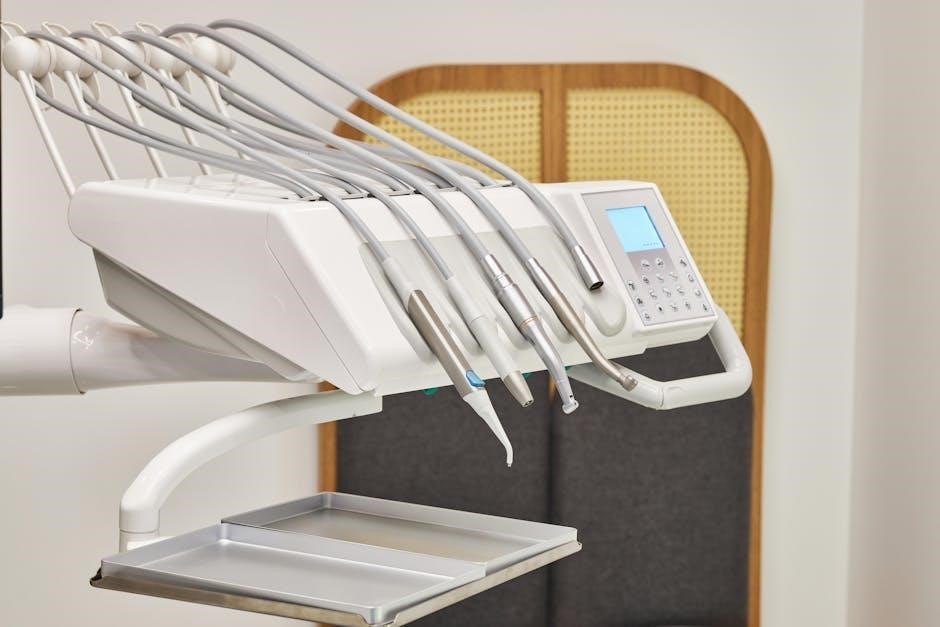

These instruments‚ often depicted in detailed PDF charts‚ require a thorough understanding of their proper angulation and technique․ Visual aids within these resources highlight subtle differences in tip shapes and handle designs․ Mastering the use of diagnostic instruments‚ as illustrated in comprehensive PDF materials‚ is fundamental to accurate diagnosis and treatment planning‚ ensuring optimal patient care․
Dental Mirrors
Dental mirrors are indispensable diagnostic tools‚ providing indirect visualization of oral tissues inaccessible by direct sight․ Comprehensive PDF guides on dental instruments invariably include detailed pictures and names of various mirror types – front-surface‚ rear-surface‚ and perioprobe mirrors – each serving specific purposes․ These PDF resources often illustrate the different head sizes and shapes available‚ impacting maneuverability and patient comfort․
PDF charts frequently detail proper mirror handling techniques‚ emphasizing angulation and lighting control․ Understanding the reflective properties and potential for distortion‚ as explained in these PDF materials‚ is crucial․ Mirrors aid in caries detection‚ assessing soft tissue inflammation‚ and verifying restorative margins․ Accurate identification‚ aided by clear pictures in PDF guides‚ is essential for effective clinical application․
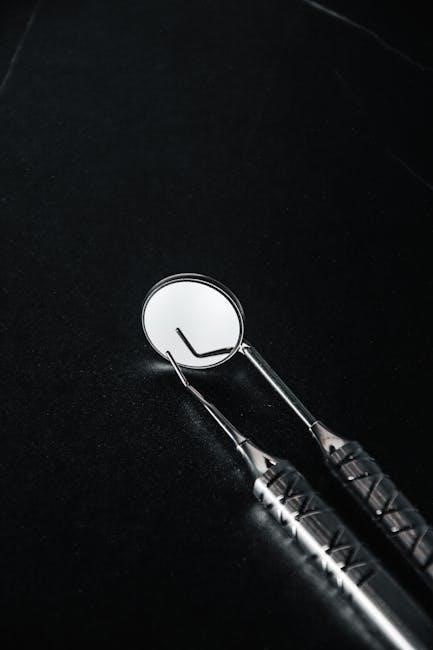

Explorers
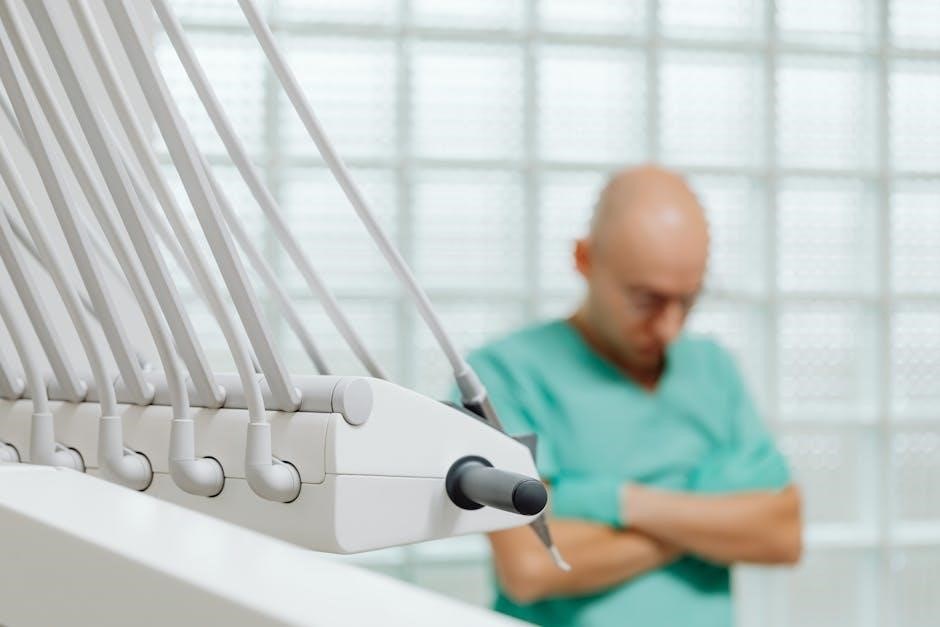

Dental explorers are vital diagnostic instruments used to detect caries‚ calculus‚ and irregularities on tooth surfaces․ PDF resources dedicated to dental instruments consistently feature detailed pictures and names of different explorer designs – such as Shepherd‚ Crane‚ and Marzavan explorers – highlighting their unique tip configurations․ These PDF guides often illustrate the correct angulation and pressure needed for effective use‚ preventing enamel damage․
Comprehensive PDF charts explain how explorers differentiate between hard and soft deposits through tactile sensation․ Proper technique‚ as demonstrated in PDF illustrations‚ is crucial for accurate diagnosis․ The pictures within these PDFs aid in identifying the working end and shank variations․ Explorers are essential for assessing restoration margins and detecting microleakage‚ skills reinforced by visual aids in detailed instrument PDFs․
Operative Instruments
Operative instruments encompass the tools used for direct restorative procedures‚ including cavity preparation and material placement․ PDF guides showcasing dental instruments pictures and names dedicate significant sections to these tools․ They detail scalers‚ curettes‚ excavators‚ chisels‚ and mallets‚ often with labeled pictures illustrating their specific applications․
These PDF resources emphasize proper instrument selection based on tooth surface and restorative material․ Detailed PDF charts explain the angulation and pressure required for efficient and safe operation․ Pictures demonstrate correct grip and technique․ Comprehensive PDFs also cover instrument sharpening and maintenance‚ crucial for longevity and effectiveness․ Understanding the nuances of each instrument‚ as presented in these PDFs‚ is fundamental for successful restorative dentistry․
Scalers
Scalers are fundamental instruments utilized for removing calculus and plaque from tooth surfaces․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides prominently feature various scaler designs‚ detailing their specific applications․ These PDF resources illustrate sickle scalers‚ used for larger calculus deposits‚ and universal scalers‚ adaptable to multiple surfaces․
PDF charts often compare and contrast different scaler types‚ highlighting blade shapes and angulations․ Detailed pictures demonstrate proper angulation and stroke techniques for effective scaling․ Many PDFs emphasize the importance of controlled pressure to avoid enamel damage․ Comprehensive guides also cover instrument sharpening‚ vital for maintaining scaler efficacy․ Learning to identify and correctly utilize scalers‚ as shown in these PDFs‚ is crucial for periodontal health and preventative care․
Curettes
Curettes are meticulously designed for subgingival scaling and root planing‚ removing tenacious calculus and smoothing root surfaces․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF resources extensively showcase universal‚ area-specific‚ and Gracey curettes‚ detailing their blade configurations․ These PDF guides often include detailed pictures illustrating blade cross-sections and their corresponding anatomical tooth surfaces․
PDF charts clarify the specific tooth surfaces each curette type is best suited for‚ aiding in accurate instrument selection․ Proper angulation and adaptation techniques are visually demonstrated within these PDFs․ Many resources emphasize the importance of a pull stroke motion for effective calculus removal․ Comprehensive PDFs also cover instrument sharpening protocols to maintain blade integrity․ Mastering curette usage‚ as depicted in these resources‚ is essential for periodontal therapy․
Excavators
Dental excavators are primarily utilized for removing caries-affected dentin during cavity preparation‚ and for condensing restorative materials․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides frequently feature detailed illustrations of various excavator designs – spoon‚ angled‚ and bin-angle – clarifying their specific applications․ These PDF resources often highlight the importance of selecting the appropriate excavator shape for optimal access and efficient caries removal․
PDF charts demonstrate proper angulation and pressure control to prevent inadvertent enamel damage․ Visual aids within these PDFs showcase techniques for safely removing soft‚ infected dentin․ Many resources emphasize the need for sharp excavator tips for precise excavation․ Comprehensive PDFs also cover instrument inspection protocols to ensure functionality․ Mastering excavator techniques‚ as illustrated in these resources‚ is crucial for conservative cavity preparation․
Chisels and Mallets
Chisels and mallets are fundamental for sectioning teeth‚ removing old restorations‚ and shaping bone during surgical procedures․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides meticulously detail the various chisel types – straight‚ angled‚ and bin-angle – alongside their intended uses․ These PDF resources often include diagrams illustrating the correct mallet striking technique to maximize efficiency and minimize trauma․
PDF charts demonstrate proper chisel angulation for controlled tooth sectioning․ Visual aids showcase techniques for removing fractured instruments or stubborn restorative materials․ Comprehensive PDFs emphasize the importance of using appropriate mallet weight and chisel sharpness․ Mastering chisel and mallet techniques‚ as illustrated in these resources‚ is vital for precise and controlled dental procedures․ Safety protocols‚ detailed in these PDFs‚ are paramount when utilizing these instruments․
Forceps
Dental forceps are crucial for tooth extraction and are categorized by jaw shape – pointed‚ blunt‚ or wing-angled – each designed for specific clinical scenarios․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides provide detailed illustrations of each type‚ clarifying their appropriate application․ These PDF resources often include comparative charts highlighting the differences between various forceps designs and their corresponding extraction techniques․
PDFs emphasize proper forceps selection based on tooth morphology and position․ Visual guides demonstrate correct grasping points to ensure stable tooth removal․ Comprehensive PDFs detail techniques for luxating and elevating teeth using forceps‚ minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues․ Mastering forceps usage‚ as shown in these resources‚ is essential for successful extractions․ Safety guidelines‚ detailed within these PDFs‚ are critical for both patient and operator safety․
Rotary Instruments
Rotary instruments‚ powered by dental handpieces‚ are fundamental for cavity preparation‚ restoration‚ and various other procedures․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF resources extensively illustrate the diverse range of burs and bits available‚ categorized by shape‚ size‚ and cutting efficiency․ These PDF guides often include detailed diagrams showcasing the cutting flutes and shank types of each instrument․
PDFs clarify the distinctions between diamond and carbide burs‚ outlining their specific applications․ Visual aids demonstrate proper bur selection based on tooth structure and treatment goals․ Comprehensive PDFs detail safe operating speeds and techniques for minimizing vibration and heat generation․ Mastering rotary instrument usage‚ as depicted in these resources‚ is vital for precise and efficient dental work․ Safety protocols‚ detailed within these PDFs‚ are paramount for both patient and operator well-being․
Dental Handpieces
Dental handpieces are essential for utilizing rotary instruments‚ driving burs and bits at controlled speeds․ Dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides dedicate significant sections to handpiece types – high-speed and low-speed – detailing their construction and functionalities․ These PDF resources often feature exploded diagrams illustrating internal components like turbines and chucks․
PDFs clarify the differences in speed ranges and torque capabilities between high-speed and low-speed handpieces‚ correlating these features with specific clinical applications․ Visual comparisons aid in understanding proper bur insertion and removal techniques․ Maintenance protocols‚ outlined in these PDFs‚ emphasize lubrication and sterilization procedures․ Comprehensive PDFs also cover handpiece coupling types and compatibility with dental units‚ ensuring optimal performance and longevity․ Proper handpiece selection‚ as shown in these guides‚ is crucial for efficient and precise dental procedures․
High-Speed Handpieces
High-speed handpieces‚ frequently detailed in dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides‚ operate at 300‚000 to 450‚000 RPM‚ primarily used for cutting tooth structure․ These PDF resources showcase various models‚ highlighting features like fiber optic illumination and tri-ple water spray systems․ Diagrams within these PDFs illustrate the internal turbine mechanism responsible for achieving such high speeds․
PDF guides emphasize the importance of proper bur selection for high-speed handpieces‚ differentiating between tungsten carbide and diamond burs․ Sterilization protocols‚ clearly outlined in these PDFs‚ are critical to prevent cross-contamination․ Proper technique‚ as demonstrated in visual aids within the PDFs‚ minimizes vibration and maximizes precision․ These PDFs also cover maintenance‚ including lubrication and routine checks‚ ensuring optimal performance and extending the lifespan of these essential instruments․
Low-Speed Handpieces
Low-speed handpieces‚ often visually represented in dental instruments pictures and names PDF resources‚ typically operate between 3‚000 and 30‚000 RPM․ These PDF guides demonstrate their versatility in procedures like polishing‚ cavity preparation‚ and orthodontic adjustments․ Detailed illustrations within these PDFs showcase different chuck types – latch-type‚ pin-and-slot‚ and quick-connect – and their corresponding bur compatibility․
PDF documentation stresses the importance of selecting appropriate attachments‚ such as contra-angle and straight handpieces‚ based on the clinical application․ Sterilization procedures‚ thoroughly explained in these PDFs‚ are crucial for infection control․ Maintenance schedules‚ also detailed in the PDFs‚ cover lubrication and inspection to ensure smooth operation․ These PDFs often include comparative charts outlining the advantages and disadvantages of various low-speed handpiece models‚ aiding in informed selection․
Burs and Bits
Dental burs and bits‚ frequently illustrated in dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides‚ are crucial rotary cutting tools․ These PDF resources categorize burs by shape‚ size‚ and cutting efficiency‚ showcasing diamond and carbide varieties․ PDF diagrams detail the anatomy of a bur – head‚ neck‚ and shank – explaining how each component influences performance․
PDF documentation emphasizes selecting the correct bur for specific tasks‚ like crown preparation or cavity refinement․ Charts within these PDFs correlate bur codes with intended uses․ Proper storage and sterilization techniques‚ outlined in the PDFs‚ are vital for maintaining bur sharpness and preventing cross-contamination․ The PDFs also cover bur mounting and dismounting procedures‚ ensuring safe operation․ Visual guides within the PDFs help identify wear patterns‚ indicating when bur replacement is necessary․
Diamond Burs
Diamond burs‚ extensively pictured in dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides‚ utilize natural or synthetic diamond particles bonded to a metallic shank․ These PDF resources detail various grit sizes – coarse‚ medium‚ and fine – correlating them to specific clinical applications like enamel cutting or finishing․ PDF illustrations showcase different diamond bur shapes‚ including round‚ pear‚ and flame‚ explaining their unique cutting characteristics․
PDF documentation highlights the advantages of diamond burs: precision‚ durability‚ and versatility․ However‚ these PDFs also caution against using diamond burs on metallic restorations․ Proper cooling with water or air‚ as detailed in the PDFs‚ is crucial to prevent overheating and diamond particle loss․ PDF charts often compare diamond burs to carbide burs‚ outlining their respective strengths and weaknesses․ Visual guides within the PDFs demonstrate proper bur handling and maintenance․
Carbide Burs
Carbide burs‚ frequently illustrated in dental instruments pictures and names PDF resources‚ employ tungsten carbide cutting edges bonded to a steel shank․ These PDF guides categorize burs by shape – round‚ tapered‚ inverted cone – and cross-cut versus straight-cut designs‚ explaining their distinct applications․ PDF diagrams showcase how different flute patterns affect cutting efficiency and debris removal․
PDF documentation emphasizes carbide burs’ effectiveness in removing hard tissues like enamel and dentin‚ and their suitability for crown preparation․ However‚ PDFs caution against their use on porcelain or acrylic․ Proper technique‚ detailed in the PDFs‚ involves light pressure and adequate cooling․ PDF comparisons highlight carbide burs’ lower cost compared to diamond burs‚ but also their tendency to dull faster․ Visual aids within the PDFs demonstrate correct bur selection and usage․
Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments‚ prominently featured in dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides‚ are crucial for oral surgery procedures․ These PDF resources detail instruments like elevators and extraction forceps‚ often accompanied by labeled diagrams․ PDFs explain the purpose of elevators – loosening teeth before extraction – and showcase various tip shapes for different clinical scenarios․
Extraction forceps‚ extensively illustrated in PDFs‚ come in various designs (e․g․‚ bayonet‚ winter) tailored to specific tooth types and root morphology․ PDF guides emphasize proper angulation and controlled force during extraction․ PDFs also cover instruments for flap design and suture placement․ Sterilization protocols for surgical instruments‚ vital for infection control‚ are thoroughly outlined in the PDFs․ The PDFs often include manufacturer details and material specifications for each instrument‚ aiding in informed selection․
Elevators
Elevators‚ frequently depicted in dental instruments pictures and names PDF resources‚ are fundamental for sectioning and loosening teeth prior to extraction․ These PDF guides showcase diverse elevator types – apical‚ physiological‚ and surgical – each designed for specific tasks․ PDF illustrations highlight the blade shapes and their corresponding applications‚ detailing how they navigate the periodontal ligament․
PDFs emphasize proper technique: controlled insertion‚ gentle pressure‚ and strategic fulcrum placement to avoid damage to adjacent structures․ The PDFs often include detailed cross-sections illustrating blade engagement․ Material composition (stainless steel) and sterilization requirements are also covered within the PDF documentation․ Understanding the nuances of each elevator‚ as presented in these PDFs‚ is crucial for minimizing trauma during extractions․ The PDFs often feature comparative charts of different elevator designs․
Extraction Forceps
Extraction forceps‚ prominently featured in dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides‚ are designed to grasp and remove teeth․ These PDF resources categorize forceps by jaw shape – root‚ bone‚ and impacted – illustrating their specific applications․ PDF diagrams clearly show the beak contours and how they adapt to different tooth morphologies․
PDFs detail proper grasping points‚ emphasizing the importance of firm‚ controlled pressure to prevent fracture․ The PDFs often include warnings about incorrect usage and potential complications․ Material (stainless steel) and sterilization protocols are standard inclusions in these PDF documents․ Understanding the nuances of each forceps type‚ as demonstrated in the PDFs‚ is vital for successful extractions․ Comparative PDF charts showcase variations in beak design and handle length․ These PDFs are essential for practical exam preparation․
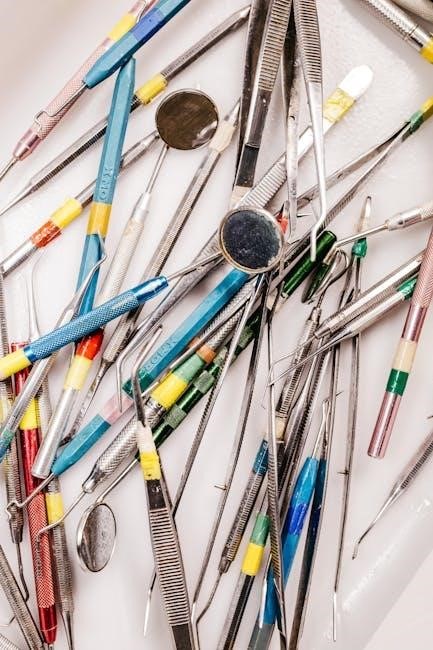

Sectional Matrices and Instruments
Sectional matrices and instruments‚ thoroughly documented in dental instruments pictures and names PDF guides‚ are crucial for composite restorations․ These PDFs illustrate various matrix bands – metallic and non-metallic – and their adaptation to different tooth preparations․ PDF resources detail the use of Tofflemire retainers‚ matrix formers‚ and burnishers‚ showcasing proper placement techniques․
PDF diagrams emphasize achieving tight proximal contacts and preventing overhangs․ The PDFs often include step-by-step instructions for wedge selection and placement‚ vital for matrix stabilization․ Material composition and sterilization guidelines are standard in these PDF documents; Mastering these techniques‚ as shown in the PDFs‚ ensures durable and esthetic restorations․ Comparative PDF charts highlight differences in matrix band contours and retainer designs․ These PDFs are invaluable for dental students and practitioners․
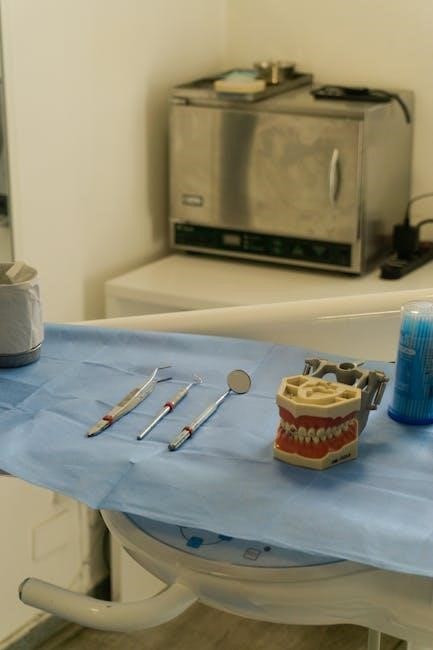
Disinfection and Sterilization of Dental Instruments
Dental instruments pictures and names PDF resources heavily emphasize infection control protocols․ These PDF guides detail the critical distinction between disinfection and sterilization‚ outlining appropriate methods for each instrument type․ PDFs illustrate the use of approved cleaning and disinfection equipment‚ adhering to EN standards‚ as mandated by manufacturers․
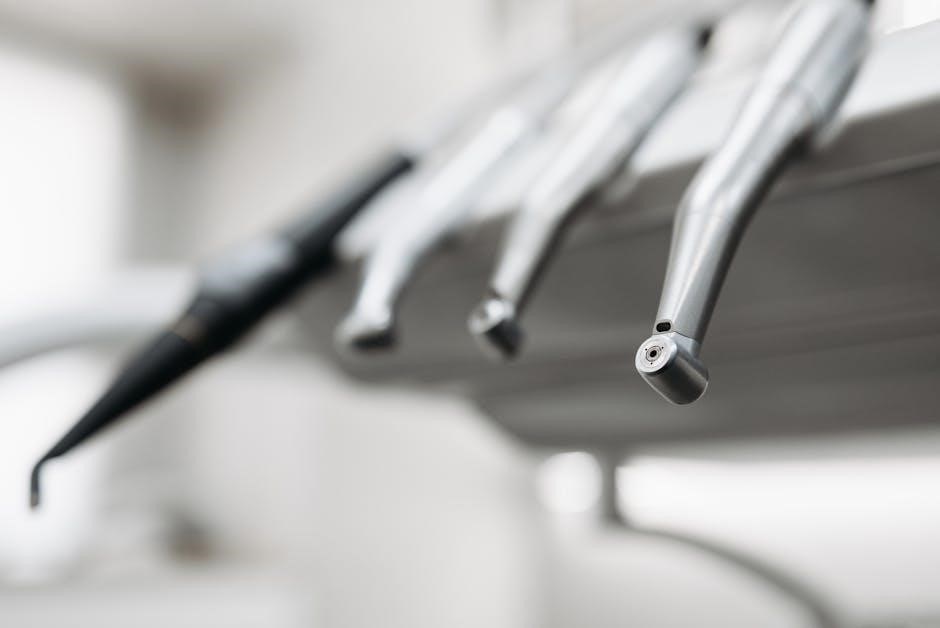

PDF charts showcase sterilization methods – autoclaving‚ chemical sterilization – and their respective validation procedures․ Proper instrument packaging and storage‚ detailed in PDFs‚ maintain sterility․ PDFs often include guidelines for handling sharps and contaminated waste․ Following these PDF-outlined protocols minimizes cross-contamination risks․ The PDFs stress the importance of regular equipment maintenance and record-keeping․ Comprehensive PDF checklists ensure adherence to best practices‚ safeguarding both patients and dental professionals․ These PDFs are essential for maintaining a safe clinical environment․
Leave a Reply